Understanding Routing and URLs in Laravel
What is Routing?
A path or URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is the address used to access a specific resource, such as a webpage or file, on a website. This process is called routing. It acts as a bridge between the domain and the content stored on the server.
Example:
If your website domain is www.example.com and you want to access a specific page like “Home,” you can define a path:
www.example.com/home
How URLs Work in Laravel
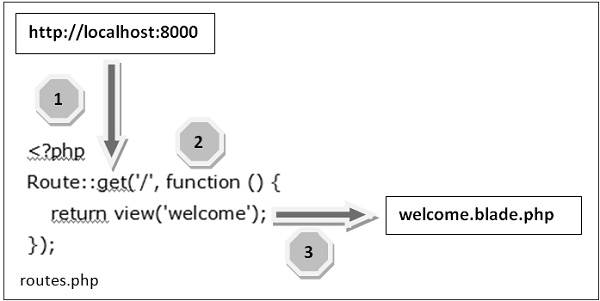
In Laravel, URLs are mapped to routes that define the logic for handling user requests. Routes direct a request to a specific function, controller, or view.
Writing a Route in Laravel
Basic Route:
Route::get('/home', function () {
return view('home');
});
This defines a route for the /home URL, which renders the home.blade.php view when accessed.
Shortcut Route for Views:
Laravel provides a shortcut for routing directly to a view:
Route::view('/home', 'home');
This performs the same action as the previous example, simplifying the syntax.
Passing Parameters in Routing
You can pass parameters to routes to make them dynamic.
Defining a Route with a Parameter:
Route::get('/home/{name}', function ($name) {
return view('home', ['name' => $name]);
});
Using the Parameter in the View:
In the home.blade.php file, you can access the passed parameter using Blade syntax:
<p>Welcome, {{$name}}!</p>
When you visit www.example.com/home/John, the page will display:
Welcome, John!
Explaining the Anchor Tag (<a>)
An anchor tag (<a>) is an HTML element used to create hyperlinks that link to other pages, files, or sections within a page.
Basic Syntax:
<a href="URL">Link Text</a>
Examples:
Linking to an External Page:
<a href="https://www.google.com">Visit Google</a>
Linking to an Internal Page:
<a href="/home">Go to Home Page</a>
Using Laravel’s route() Helper
Laravel provides a route() helper to generate URLs for named routes.
Defining a Named Route:
Route::get('/home', [HomeController::class, 'index'])->name('home');
Generating a URL in a Blade Template:
<a href="{{ route('home') }}">Go to Home</a>
Adding Parameters to the Link
If your route expects a parameter, you can pass it using the route() helper:
Defining a Route with a Parameter:
Route::get('/home/{name}', [HomeController::class, 'index'])->name('home');
Generating a URL in a Blade Template:
<a href="{{ route('home', ['name' => 'John']) }}">Welcome John</a>
This will generate a URL like:
www.example.com/home/John
Conclusion
Routing in Laravel is a powerful feature that allows developers to define and manage application URLs easily. With support for parameters, named routes, and the route() helper, Laravel makes routing both flexible and efficient.